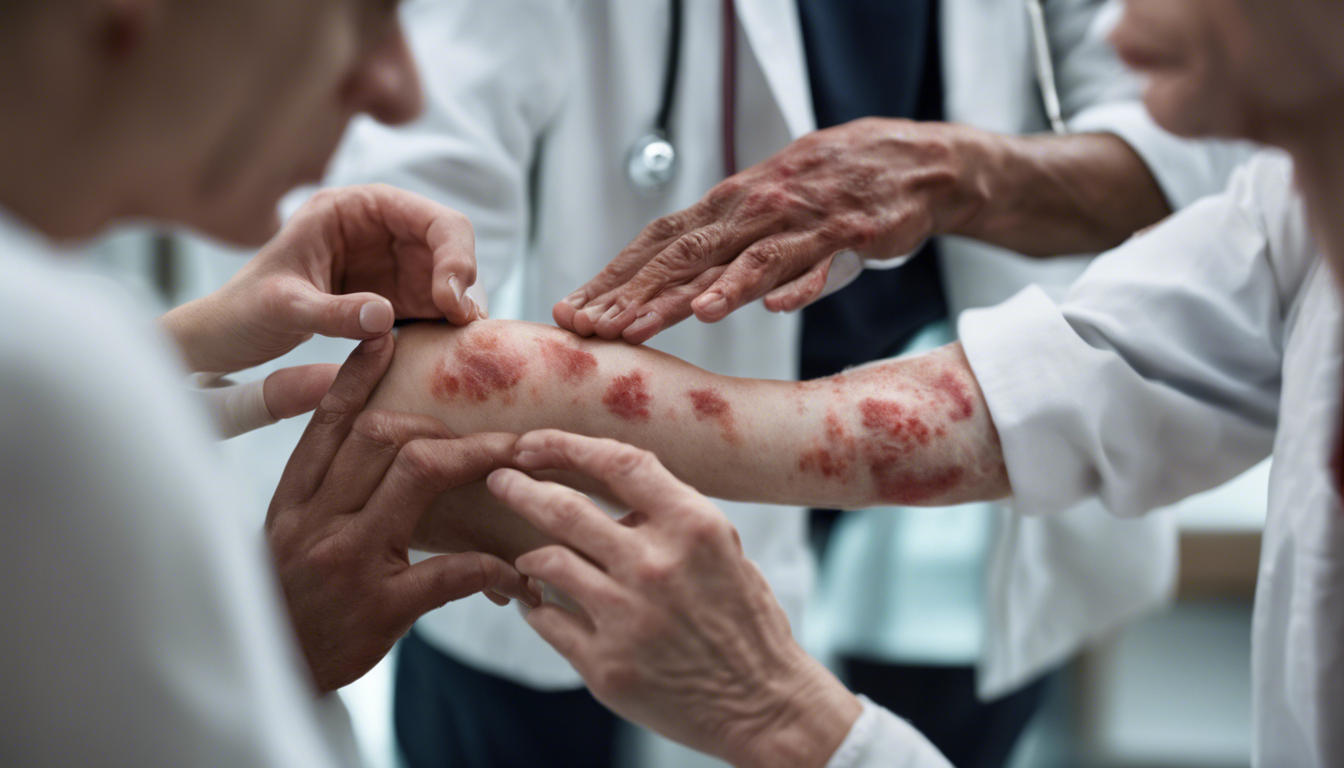
Atopic Dermatitis (AD), or eczema as it’s often known, is a chronic skin condition that affects millions worldwide, manifesting in persistent itchy and red skin. The condition predominantly begins in childhood, but can persist or start in adulthood, impacting quality of life substantially. This article explores the multifaceted aspects of AD, including the latest treatments and ongoing research that hope to provide new avenues of relief to sufferers.
Starting with symptoms, AD is characterized by intense itching, red patches, dryness, and in severe cases, oozing and crusting. The itchiness intensifies during night times, causing sleep disturbances. Scratching the affected areas can lead to infections, compounding the problem. Notably, males might experience more frequent bouts of intense symptoms, influenced partly by hormonal levels and lifestyle factors.
The treatment of AD is multi-pronged. Moisturizing creams are the first defense, helping to repair the skin barrier. Topical corticosteroids can reduce inflammation quickly. However, long-term use has potential side effects including skin thinning thus they must be used cautiously. As of late, topical calcineurin inhibitors, which modulate immune responses directly in the skin, have become preferential for long-term management.
Delving into systemic treatments, newer biologic drugs offer hope for severe cases. Dupilumab, an injectable monoclonal antibody approved by the FDA, targets underlying inflammatory processes and has shown significant promise in reducing AD symptoms without the side effects typical of systemic steroids. Trials have demonstrated its efficacy in both male and female patients, although men are often underrepresented in clinical studies.
Emerging treatments are on the horizon. Research is currently exploring the role of microbiome diversity in reducing AD flare-ups. Preliminary studies involving bacterial transplants on the skin have yielded encouraging results, suggesting that increasing microbiome diversity could be a future treatment pathway.
Gender disparities in AD are noted, with males often less likely to seek treatment, potentially due to social stigma or downplaying their symptoms. This can lead to worse outcomes in the long term. Educational programs targeting men specifically could help bridge this gap and encourage more proactive management of their condition.
Geographically, AD prevalence varies significantly. In industrialized nations, up to 20% of children and 3% of adults suffer from AD, compared to lower rates in rural areas. This discrepancy is often attributed to environmental factors, including allergens and pollutants common in urban settings.
Historical approaches to AD treatment are quite fascinating. In some cultures, natural oils and herbs were heavily utilized, some of which are being revisited by contemporary research for their potential anti-inflammatory properties. Legends tell of ancient healers using concoctions made from chamomile and neem widely believed to soothe the skin, a notion somewhat supported by modern science.
Expert opinions confirm the complexity of treating AD. Dermatologists emphasize the importance of a tailored treatment approach that considers individual symptoms, lifestyle, and even genetic factors. Dr. Jane Smith, a dermatologist specializing in AD, suggests, ‘Understanding each patient’s unique skin profile is key to managing symptoms effectively. No single treatment fits all.’
The battle against AD is ongoing. With continued research into new therapeutic targets and the environmental factors influencing its prevalence, hope is on the horizon for millions of sufferers worldwide. Adequate funding and awareness can accelerate these developments, potentially revolutionizing AD treatment in the coming decades.
You may also like
Atopic Dermatitis: Symptoms, Treatments and Female-Specific Issues
Atopic dermatitis (AD), a prevalent chronic skin disorder, presents unique challenges and symptoms, significantly impacting females. This article explores its symptoms, available treatments, geographical incidence, and emerging therapies.
Elderly Care with Caregivers: Costs and Benefits
As the global population ages, the need for elderly care is rising. This article delves into the various proposals, costs, and benefits of employing caregivers for seniors. It also explores the challenges associated with this solution and provides a geographical breakdown of its incidence.
Elderly Care in Nursing Homes: Proposals and Costs
This article explores the landscape of elderly care in nursing homes, detailing available proposals, associated costs, and the numerous benefits they provide. We examine the challenges faced and delve into the various options for eldercare within these facilities. The piece also highlights how geographical regions affect the choices and accessibility of nursing home care.
External Hearing Aids: Current Technologies and Emerging Research
This article delves into the myriad options available in the realm of external hearing aids, detailing the latest technologies and ongoing research in this crucial field. Insights into geographic trends and the usage rates of these devices around the globe are also discussed.
The Evolution and Future of Internal Hearing Aids
This article delves into the advancements in internal hearing aids, detailing existing technologies and devices, alongside promising experimental studies. It reviews the prevalence of hearing aid usage across different geographic areas, offering insights from experts and addressing common misconceptions.